Getting Started with I2C: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
What we are going to talk about: | What we are going to talk about: | ||
* I2C | * I2C | ||
* DS3231 | * DS3231 Real Time Clock (RTC) | ||
* AT24C32 | * AT24C32 32Kbit EEPROM (4096 bytes) | ||
* TM1637 | * TM1637 7-segment LED driver (decimal points or colon) | ||
* Logic8 / Logic16 | * Logic8 / Logic16 logic analyzer | ||
Begin by watching the following "Understanding I2C" video: | |||
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CAvawEcxoPU | |||
1) What is I2C - The bus hardware | 1) What is I2C - The bus hardware | ||
2) START and STOP conditions (These are NOT bits) | 2) START and STOP conditions (These are NOT bits) | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
4) Acknowledge bit (receiver of data provides acknowledge) | 4) Acknowledge bit (receiver of data provides acknowledge) | ||
5) What isn't I2C? Examine the TM1637 | 5) What isn't I2C? Examine the TM1637 | ||
5) | 5) Examine the DS3231, write and read it's registers | ||
6) | 6) Examine the AT24C32, write and read data | ||
==DS3231 Module== | ==DS3231 Module== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 22: | ||
https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ds3231.pdf | https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ds3231.pdf | ||
https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ds3231m.pdf (The 'M' variant) | https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ds3231m.pdf (The 'M' variant) | ||
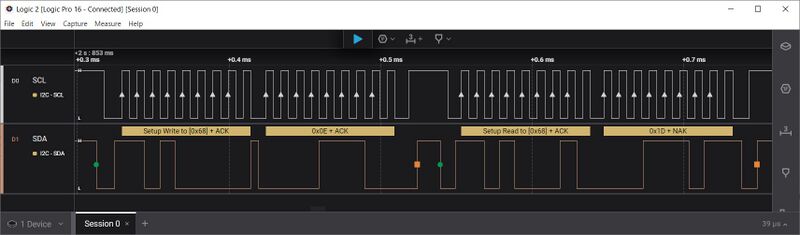
'''Reading DS3231 control register (0x0E)'''<p> | |||
[[FILE:i2c_ds3231_read_write.jpg|800px]] | |||
===AT24C32=== | ===AT24C32=== | ||
This 32Kbit EEPROM (4096 x 8), will hold 4096 bytes of data. | This 32Kbit EEPROM (4096 x 8), will hold 4096 bytes of data. | ||
https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/doc0336.pdf | https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/doc0336.pdf | ||
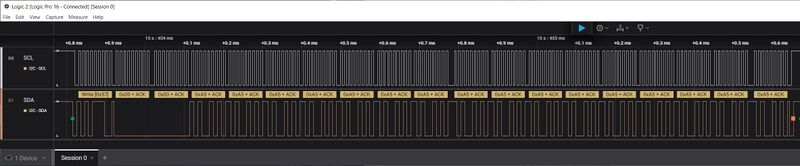
'''Writing 16 bytes using page write'''<p> | |||
[[FILE:AT24C32_write_16_bytes_using_page_write.jpg|800px]]<p> | |||
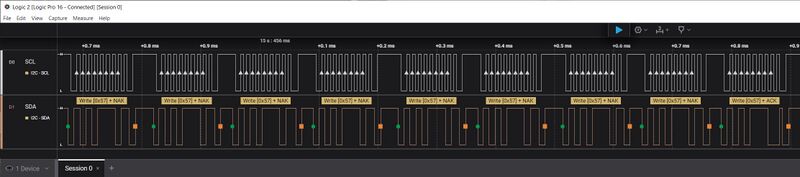
''Following a write, polling the device, waiting for ACK to signal device is ready'''<p> | |||
[[FILE:AT24C32 poll-for ready.jpg|800px]] | |||
==TM1637== | |||
Multiple 7-segment LED display driver / keypad scanner | |||
https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256801873805909.html (decimal points) | |||
https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256801704898010.html (decimal points) | |||
https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256801873036951.html (colon) | |||
'''Waveforms captured during a clock update'''<p> | |||
[[FILE:TM1637 - Updating Clock-Time Display.jpg|800px]] | |||
==The Software== | |||
'''Arduino Example:''' | |||
https://github.com/JimMerkle/Arduino_Uno_Command_Line_I2C_DS3231_TM1637 | |||
'''NUCLEO-F103RB Example:''' | |||
https://github.com/JimMerkle/NUCLEO-F103RB_TM1637_DS3231_Clock | |||
==References== | |||
https://www.analog.com/en/resources/technical-articles/i2c-primer-what-is-i2c-part-1.html | |||
https://www.ti.com/lit/an/sbaa565/sbaa565.pdf | https://www.ti.com/lit/an/sbaa565/sbaa565.pdf | ||
https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ds3231.pdf | https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ds3231.pdf | ||
https://www.arduino.cc/en/uploads/Main/Arduino_Uno_Rev3-schematic.pdf | https://www.arduino.cc/en/uploads/Main/Arduino_Uno_Rev3-schematic.pdf | ||
Latest revision as of 15:53, 23 January 2025
Agenda
What we are going to talk about:
- I2C
- DS3231 Real Time Clock (RTC)
- AT24C32 32Kbit EEPROM (4096 bytes)
- TM1637 7-segment LED driver (decimal points or colon)
- Logic8 / Logic16 logic analyzer
Begin by watching the following "Understanding I2C" video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CAvawEcxoPU 1) What is I2C - The bus hardware 2) START and STOP conditions (These are NOT bits) 3) I2C Address and the R /W bit - (7 or 8 bit I2C address ?) 4) Acknowledge bit (receiver of data provides acknowledge) 5) What isn't I2C? Examine the TM1637 5) Examine the DS3231, write and read it's registers 6) Examine the AT24C32, write and read data
DS3231 Module
DS3231
The time (and temperature), are accessed via 19 byte-wide registers, see Address Map on page 11. https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ds3231.pdf https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ds3231m.pdf (The 'M' variant)
Reading DS3231 control register (0x0E)
AT24C32
This 32Kbit EEPROM (4096 x 8), will hold 4096 bytes of data. https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/doc0336.pdf
Writing 16 bytes using page write
Following a write, polling the device, waiting for ACK to signal device is ready'
TM1637
Multiple 7-segment LED display driver / keypad scanner https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256801873805909.html (decimal points) https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256801704898010.html (decimal points) https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256801873036951.html (colon)
Waveforms captured during a clock update
The Software
Arduino Example: https://github.com/JimMerkle/Arduino_Uno_Command_Line_I2C_DS3231_TM1637 NUCLEO-F103RB Example: https://github.com/JimMerkle/NUCLEO-F103RB_TM1637_DS3231_Clock
References
https://www.analog.com/en/resources/technical-articles/i2c-primer-what-is-i2c-part-1.html https://www.ti.com/lit/an/sbaa565/sbaa565.pdf https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ds3231.pdf https://www.arduino.cc/en/uploads/Main/Arduino_Uno_Rev3-schematic.pdf