STM32 - WIZnet W5500
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The WIZnet W5500 Ethernet chip provides an easy Ethernet network solution for many microprocessors/microcontrollers. Using a SPI interface and sample library code, most any processor can use this device to get connected to a network.
Hardware Interface
In my case, I purchased a small development module from Amazon.com. This same module is readily available on Ebay.com and Aliexpress.com Examples: https://www.amazon.com/AITRIP-Ethernet-Hardware-Microcontroller-Interface/dp/B09FG5VZFS/ref=sr_1_10 https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256801465688850.html A 10 conductor, 2x5 pin header, provides the electrical connection between the host and this module I wired mine using a female-female ribbon cable as follows: Wire Color Signal W5500 Module Pin NUCLEO-F103RB Pin Comment Brown Not Connected J1-1 NC Red SPI-SCLK J1-2 SCLK SPI2_SCK, PB13, CN10-30 Orange INTn J1-3 INT PB11, CN10-18 Active low Yellow SPI-CSn J1-4 SCS SPI2_NCS, PB12, CN10-16 Active Low Chip Select Green RSTn J1-5 nRST PB10, CN10-25 Active Low, 500us min Blue MOSI J1-6 MOSI SPI2_MOSI, PB15, CN10-26 Violet GND J1-7 GND GND, CN10-20 Grey MISO J1-8 MISO SPI2_MISO, PB14, CN10-28 White 5.0V (NC) J1-9 NC Black 3.3V J1-10 3.3V +3V3, CN7-16 Information in the comment field describes what pin/function I connected to on my NUCLEO-F103RB board.
Target Software Interface
The WIZnet software library, "ioLibrary_Driver-master", https://github.com/Wiznet/ioLibrary_Driver interfaces to the target via function pointers. Need to implement the following functions (function name not important): void W5500_Select(void); // Drive the SPI-CSn signal low, selecting the device void W5500_Deselect(void); // Drive the SPI-CSn signal high, deselecting the device void W5500_WriteByte(void); // Write a single byte to the device uint8_t W5500_ReadByte(void); // Read a single byte from the device void W5500_WriteBuff(uint8_t* buff, uint16_t len); // Write one or more bytes from a buffer void W5500_ReadBuff(uint8_t* buff, uint16_t len); // Read one or more bytes into a buffer For DHCP, a couple call-back functions need implementations: void Callback_IP_Assigned(void); void Callback_IP_Conflict(void);
SPI Interface Configuration
The SPI interface, host side, is configured to use SPI2 (SPI1 has LED2 in conflict with SPI1_SCK). Mode: Full-Duplex Master Hardware NSS Signal: Diable (We will manage the active low chip select, NCS signal, with software) Frame Format: Motorola Data Size: 8-bits First Bit: MSB First Prescaler: 32 - This creates a 1.125MBits/sec SCK Clock Polarity (CPOL): Low Clock Phase (CPHA) 1 Edge (First Edge) CRC Calculation: Disabled NSS Signal Type: Software
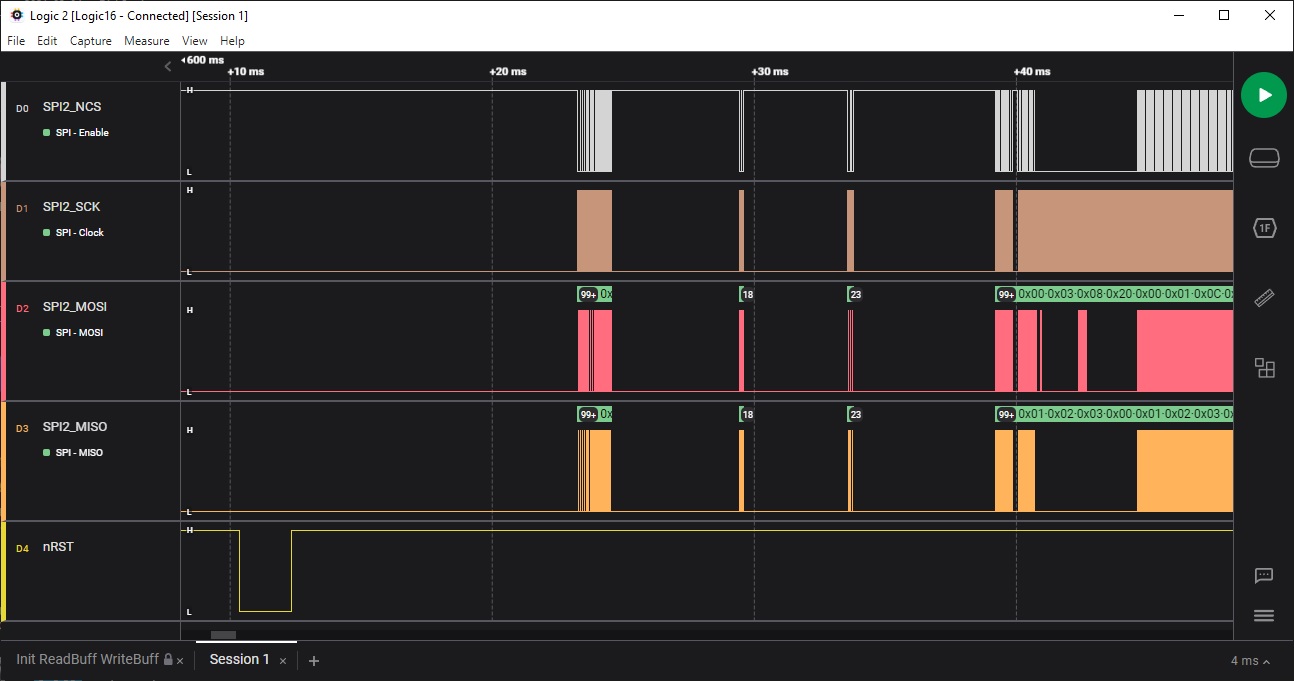
SPI Interface Captures
Although some example code doesn't use the hardware reset, I manage a hardware reset using PB10.Examining the first frame of data transfer with the device
It's interesting to see the 0x01, 0x02, 0x03 on the MISO signal immediately following NCS. View showing blocks of data being transferred in different periods of time following reset.
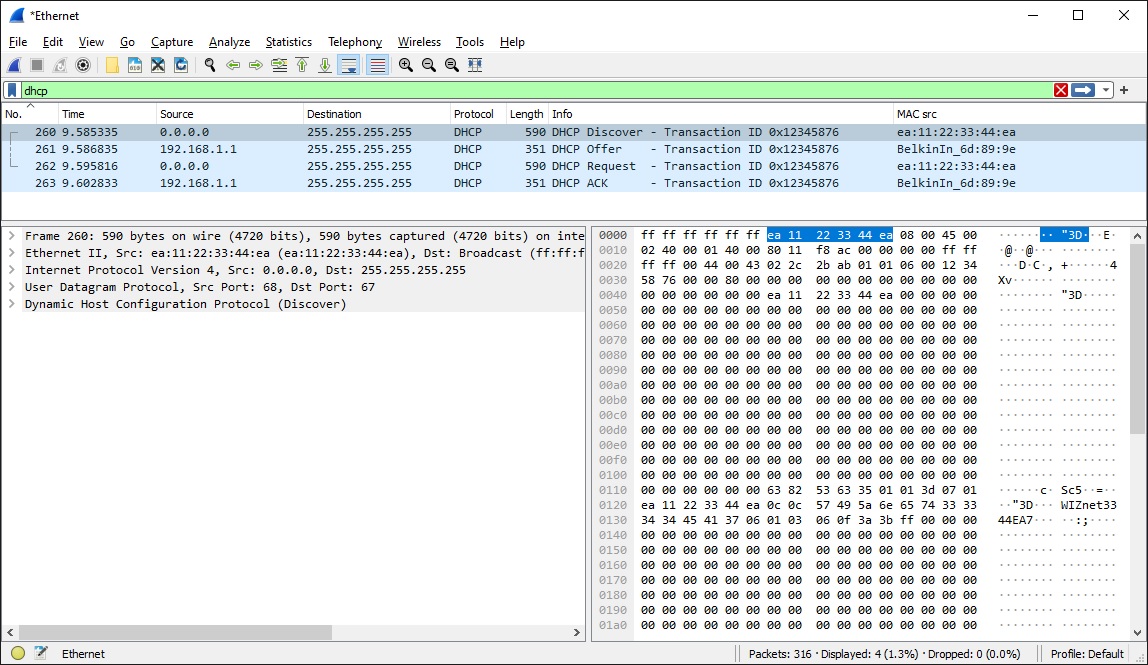
Wireshark View
Wireshark display of DHCP capture (managed network switch with port mirroring required):
Calling w5500_init() from command_line
>init w5500_init() w5500_hardware_reset() Registering W5500 callbacks... Calling wizchip_init()... wizchip_sw_reset() wizchip_init() Success! PHY Link Up PHY Link Time: 1531ms Calling DHCP_init()... w5500_init(), MAC:EA 11 22 33 44 EA Registering DHCP callbacks... Calling DHCP_run()... IP assigned! Leased time: 86400 sec DHCP Time: 3884ms IP: 192.168.1.126 GW: 192.168.1.1 Net: 255.255.255.0 DNS: 192.168.1.1 Calling wizchip_setnetinfo()... Calling DNS_init()...